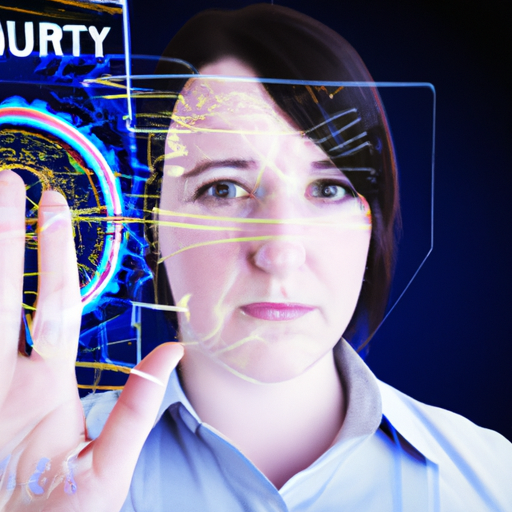
In an age where data breaches and identity theft are increasingly common, biometric security has emerged as a frontline solution to enhance identity verification processes. This technology uses unique biological traits—like fingerprints, facial recognition, and iris patterns—to authenticate individuals, making it a powerful tool for safeguarding personal and organizational data.
What is Biometric Security?
Biometric security refers to the advanced methods of securing systems and data through the unique physical characteristics of individuals. This technology allows for more accurate identification compared to traditional passwords or PIN codes, leading to a higher level of security. Common biometric methods include:
- Fingerprint authentication
- Facial recognition
- Retina scan
- Voice recognition
Innovations in Biometric Technology
Recent technological innovations have significantly enhanced the capabilities and applications of biometric security. Here are some of the most noteworthy trends:
1. Multi-Modal Biometrics
Integrating multiple biometric traits (e.g., combining facial recognition with voice verification) increases security by creating a more robust authentication process. This reduces the risk of false positives and enhances the reliability of identity verification.
2. AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence is being utilized to improve the accuracy of biometric systems. Machine learning algorithms are trained to recognize subtle variations in biometric data, thus increasing accuracy and reducing fraud.
3. Mobile Biometric Solutions
As smartphones become ubiquitous, mobile biometrics are on the rise. Features like fingerprint scanners and facial recognition on mobile devices provide users with secure and convenient access to their personal information.
Applications of Biometric Security
The applications of biometric security are vast, spanning various industries:
- Finance: Banks are adopting biometric authentication for secure transactions, reducing fraud, and protecting user accounts.
- Healthcare: Biometric identifiers secure patient records and ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive information.
- Travel: Airports are increasingly using facial recognition technology to streamline the passenger boarding process and enhance security.
Challenges Ahead
Despite its benefits, biometric security faces several challenges, including privacy concerns and data protection. Implementing strong governance around the use of biometric data is crucial to maintaining public trust.
Conclusion
As we move forward, the demand for biometric security solutions will continue to grow, driven by the need for enhanced security measures in our increasingly digital world. Companies that invest in this technology will not only improve security but also enhance user experience, making biometric authentication a vital component of modern security architecture.
Stay tuned for more updates on the evolving landscape of biometric security technology. The future looks promising, with continuous innovation and applications ready to reshape how we think about security.